China is one of the most populous countries in the world. To your surprise, the population of China is more than the combined population of four regions like the US, Canada, Australia, and Europe excluding Russia. China is native to 56 ethnic groups which played a great role in the development of various languages spoken in China.
People speak multiple languages in different geographical locations like main China and countries like Tibet, Hong Kong, and Taiwan. Mandarin Chinese is the most popular language in China. It is native to 955 million people out of the whopping population of 1.21 billion people.
China is a Linguistic Diverse Country
China is one of the linguistically diverse countries in the world. According to the Ethnologue survey, there are 302 living languages in China. Out of these 276 are native. To recognize and celebrate cultural diversity, the United States observes 20 April as Chinese language day to promote the six official languages of the country.
When we see the historical background, April 20 is also a day on which Chinese people honor Cangiie. Chinese legends consider this figure because they think they have invented the Chinese characters.
According to the ancient Chinese text Huai-nan-zi, Chinese writing was invented when millet which is a type of grain rained from heaven and spirits cried at night. Due to political reasons, Chinese people have categorized their languages on the based-on dialects.
The Chinese language is from the family of Sino-Tibetan languages. It is the largest group of language families from around the world. The Chinese language is native to 1.3 billion people from around the globe. Mandarin is one of the famous dialects of the Chinese language.
Therefore, people speak it widely. The other famous dialect of the Chinese language is Cantonese. People who speak Mandarin cannot understand it. Each dialect that people speak in China is unique. However, despite the uniqueness of various dialects, Mandarin Chinese or Putonghua has been the official language of China since the 1930s.
National Language of China
Standard Chinese is the official language of China. People also called it modern standard Mandarin and standard Mandarin. This language is a dialect of Mandarin language and contains characteristics of other dialects. It contains the aspects of Chinese grammar in its written form.
Moreover, for the proper pronunciation of words, people use the Beijing dialect. In the center of China, Standard Chinese is called Putonghua whereas in Taiwan it is called Guoyu which means national language. In 1949, the Chinese government decided to have one official language. Therefore, they passed different laws to implement the national language in 1955.
The use of Standard Chinese in mainland China is controlled by the national language regulating committee whereas the language spoken in Taiwan is controlled by the national language committee. The national language regulating committee has made the Chinese language the national language of the country. Therefore, people use the national language to communicate with other varieties of the Chinese language.
China’s national policy has given autonomy to different regions to use their dialect of the language. Moreover, they must speak and understand the national language Mandarin. When the Mandarin language is selected as a national language then in the same year, the law is passed to teach the language in all the educational institutions of the country. This made all the people use this language in all the fields of life. This law also made changes in Chinese characters.
The Chinese government has also declared a law which is the National Common language and writing law which states the requirements for the promotion of standard Chinese in the country. China’s ministry of education conducted a survey that shows that 70% of the population in mainland China can speak standard Chinese.
Moreover, out of this number, only 10% can eloquently speak the language. People of China and Taiwan use this language in the education system and the government aims to integrate the language up to 80% in the country. As far as the written style of the Chinese language is concerned, it is using the simplified Chinese characters called Putonghua and the traditional language characters called Guoyu.
Official Language of China
The other official language people speak in China is Cantonese. This language came into existence in the port of Guangzhous and from the port, this language is spread in Peral River Delta. This language has got a name from Guangzhous which is also called Canton. Cantonese is also an official language of Hong Kong. According to Hong Kong law, all government and law agencies use this language.
Cantonese is also the official language of Macau. It is an important variant of the Chinese language. Moreover, it is part of the dialect called Yue. Cantonese is native to 80 million people in China. It is the official language in the state of Guangxi.
Cantonese has three dialects: Hong Kong dialect, Macua dialect, and Guangzhou dialect. The name of these dialects is geographically based. It is written with traditional and vernacular Chinese characters.
The Chinese language Dialects
There are many Chinese dialects. Sometimes it is very hard to identify different dialects. However, according to linguists, there are seven main dialects of the Chinese language. Mandarin is one of the popular and main dialects. Other dialects are further divided into sub-dialects.
One important thing to note is that these dialects are not mutually intelligible. This is because of the reason that the different regions in China are far away from each other. Therefore, they are not in contact with each other. So they only understand the dialect spoken in their region. However, millions of people speak these dialects.
It is a very daunting task to understand the diversity and complexity of Chinese languages. Due to different accents, the pronunciation of different characters is different.
Let’s have a look at different Chinese dialects.
Mandarin
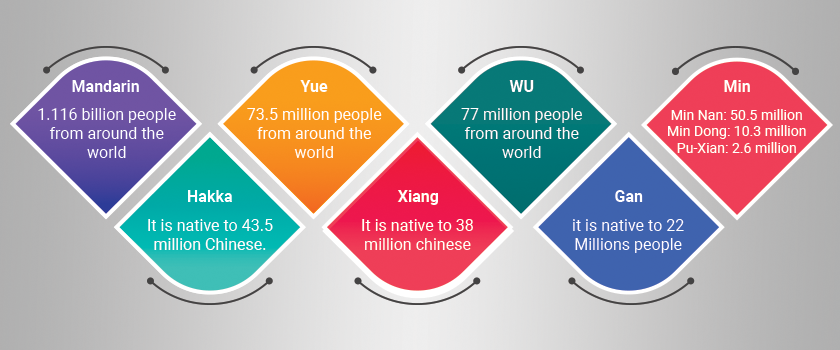
Two-third of the Chinese population speaks Mandarin. Therefore, it is the top-most spoken language in China. The other name of Mandarin is Beifang Fangyan, Zhongguohua, Beijinghua, and standard Chinese. Approximately 1.082 billion people speak Chinese as a first and second language. Moreover, 1.116 billion people from around the world speak this language. Let’s have a look at four subdivisions of Mandarin Chinese.
Southwestern Mandarin- People living in the province of Southwest China, Yunnan, Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guizhou speak Southern Mandarin.
Southern Mandarin- People living in the province of Nanjing, Hainan, and Guangdong speak southern mandarin.
North-western Mandarin- People living in Baoji and people living in the northwest provinces like Qinghai, Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia, and Xinjiang speak North-western mandarin.
Northern Mandarin- People living in the Northeast provinces, Northern China, and Beijing speak northern mandarin.
Mandarin has four tones that are level, rising, high-rising, and falling. These tones help in identifying the words that have the same consonants and vowels but different meanings. It is important to note that there are very few words in Mandarin that end with a consonant. It uses monosyllabic words. Moreover, it contains fixed word order because there are no parts of speech that show inflection.
Yue
Yue is from a group of similar Sinitic languages. People living in Southern China like Guandong and Guangxi speak this language. The other name of this dialect is Cantonese. It represents the entire group however linguists used this name for the dialects that people speak in the areas of Wuzhou,Guangzhou, and Macau.
It comes after Mandarin in terms of its speakers. Around 62 million people in China and 73.5 million people from around the world speak this language. People living in Guangdong speak this dialect because of the immigrants who came to reside there. The majority of immigrants in the 20th century used to speak Yue or Cantonese.
It has 10- sub-dialects and the standard dialect is Guangzhou. Cantonese is like old Chinese especially in the use of consonants. It possesses six tones. Moreover, its initial consonants and syllables are different from each other.
Wu
Wu is the Chinese dialect. People living in the coastal area in Shanghai speak this language. Moreover, people living in Zhejiang province, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi, and Jiangsu also speak this dialect. Major Wu dialects include Wuxi, Changzhou, Suzhou, Jinhua, Yongkang, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Shoaxing, Hangzhos, Ningbo, and Shanhai .
It is the second most variant of the Chinese language. Approximately, 77 million people speak the Wu dialect. In the 5th century, this dialect got popularity from the cultural center called Suzhou. Moreover, it gained more recognition in the era of the Ming Dynasty.
It uses seven or eight tones to identify the different words with the same vowels and consonants. The Wu speakers, who use Lu Xun, Cai Yuanpei, and Chiang Kai-shek hold a great position in Chinese politics and culture.
Min
Min is the Chinese dialect. People living on the southern coast of China, Fujian speak this language. It is the most diverse dialect because the pronunciation of words is different. The Min name is derived from the Min River that is in Fujian. The sub-dialects in Min are not mutually intelligible. The Min has five variants.
Min Nan: Min Nan is native to 50.5 million speakers. These speakers are present in South-eastern China and Taiwan. The other sub-dialects of Min Nan include Xiamen and Amoy. People use this dialect in trade dealings.
Min Bei: People living in China and Singapore use this dialect widely.
Min Dong: Approximately 10.3 million people speak this dialect.
Min Zhong: Another name of this dialect is Central Min. People from different communities like Yong, and Sanming speak this dialect in the province of Fujian.
Pu-Xian: Around 2.6 million people speak this dialect. People living in Malaysia and Singapore speak this dialect.
The grammar and vocabulary of Min came into existence with the help of the diverse linguistic history of China. Although there are many speakers of Min, the history of its development has made it difficult to identify Chinese characters.
This is because of the reason that Chinese characters are mainly designed for the Mandarin language. Therefore, written Min uses Roman characters when Mandarin characters are not available. Tang Min is the name of the pronunciation system of Min.
Hakka
Hakka is a Chinese dialect. People living in isolated areas speak this dialect. Due to this reason, it has 13 sub-dialects that are different from each other. It is native to 43.5 million Chinese. People living in eastern and north-eastern parts of Guangdong province like Hunan, Hainan, Guangxi, and south Jiangxi speak this language.
Moreover, people living in western and southwestern parts of Sichuan provinces also speak this language. The speakers of Hakka are present in Taiwan, French, Guiana, Hongkong, Cambodia, and Brunei. Moreover, in other countries like Singapore, Thailand, Suriname, Indonesia, and Panama, people speak the Hakka language widely. The Hakka has six tones and it borrowed many words from Cantonese. Furthermore, it is similar to Gan.
Xiang
The Xiang is the Chinese dialect. People of the Southern province of China, Hunan speak this dialect. Mandarin-speaking people are present around this area. Therefore, Hakka has a great impact on the Mandarin language. Moreover, Hakka is very similar to Mandarin.
This language is further categorized into two parts that are old and new Xiang. The people of Shuangfeng and Hunan speak old dialects whereas the people of Hunan’s capital Changsha speak a new dialect. Old Xiang has many similarities with the Wu dialect. Xiang has five tones and contains different consonants.
Gan
Gan dialect is similar to Hakka. It is native to 22 million people. These people reside in the provinces of Hubei, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Hunan. People residing in Hubei speak a Gan dialect called Jiangxinese, Kan, or Xi. It contains an old vocabulary that is no longer applicable in Mandarin. Due to its similarity with Hakka, Hakka speakers can understand Gan easily.
Wrapping Up
By now you are aware of the different languages spoken in China. For the translation and interpretation of these languages, you must hire a professional translation company. This is because of the reason that professional translation companies have a team of native translators who are aware of cultural and regional nuances. Moreover, they know the variation among different Chinese dialects. Therefore they provide you with impeccable chinese translation services in a fast turnaround time.
Resources
How Many Languages are Spoken in China
How Many Languages are Spoken in India
What Languages are Spoken in Brazil?
What Languages are Spoken in Israel?
What Language is spoken in Iceland?
What Languages Spoken in the Philippines
Most Spoken Languages in Africa
Most Endangered Languages in the World
Official Languages of the United Nations
most useful languages for Business?
Exploring the Languages of Future